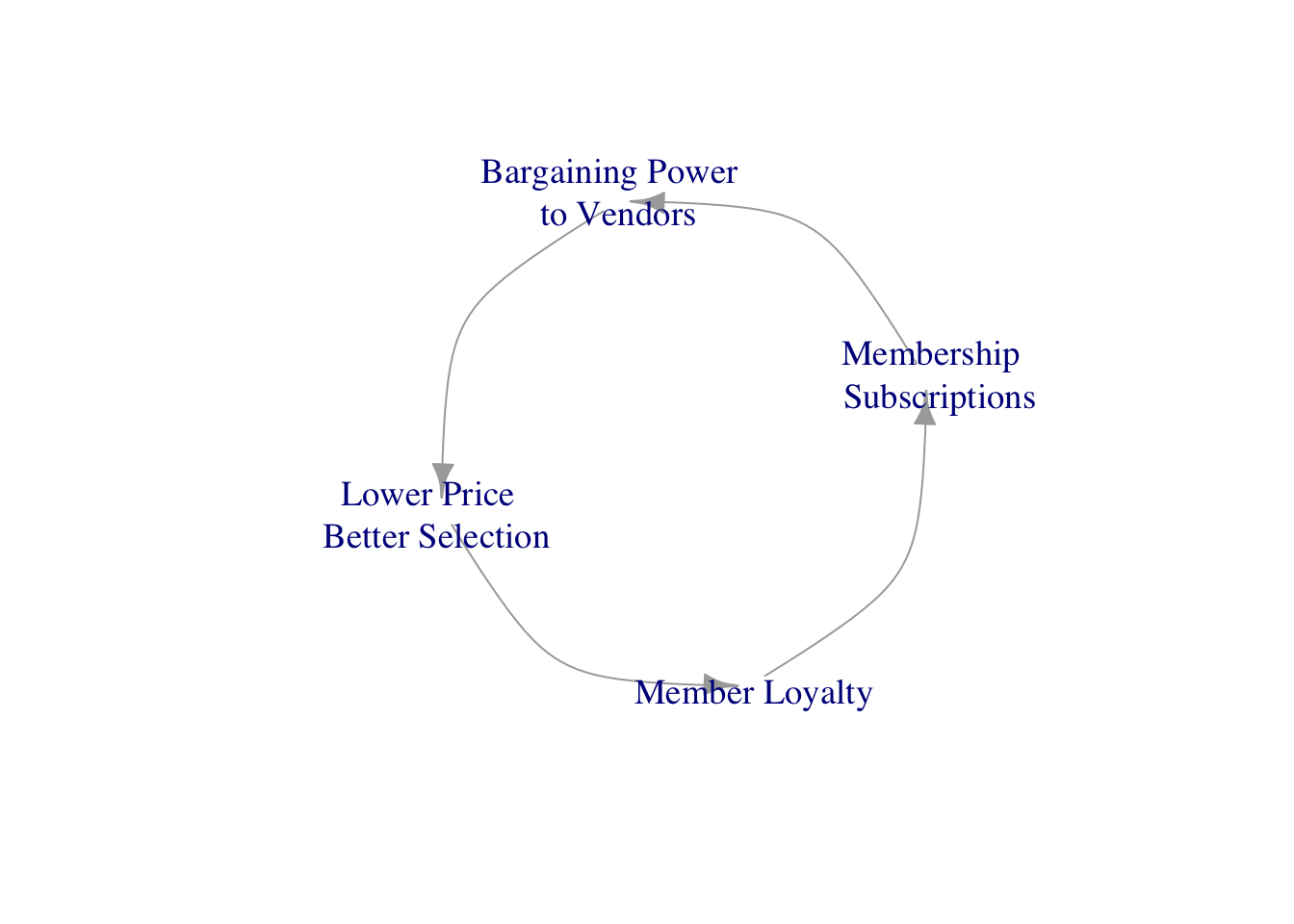
Costco’s membership renewal rates in the united states and Canada have remained at roughly 90%. The traffic-driving value that Costco offers in its stores is fueled by cost leverage that, in turn, feeds additional store visits.
Costco has achieved a competitive advantage based on its intangible assets and cost leadership. The firm’s membership subscription model has held steady through the financial crisis and the rising competitions, especially Amazon’s Prime memberships. In addition to cost management and distribution leverage, Costco’s low prices are enabled by its procurement strength.
Costco sells roughly 3,700 different stock-keeping units (SKUs) in its stores, a fraction of the 75,000 to 80,000 at Walmart in the United States, which offers a significantly greater number of items via its marketplace. Costco’s sales per SKU were over 30 million, towering above Walmart’s less than 3 million and Target’s $1 million, contributing to its procurement cost advantage.
Costco benefits from a number of traffic drivers, particularly its food offerings (53 % of fiscal 2019 sales) and fuel. Fuel sales serve as a meaningful counterpoint to traffic pressure from digital sellers. With in-store prepared food offerings and a well-developed private-label portfolio, Costco’s store offering is well distinguished. With in-store ready food offerings, the Kirkland signature brand accounts for around a quarter of Costco’s sales and is also margin-accretive.
Costco has been increasing its e-commerce efforts (roughly 4% of sales), focusing on items not available in stores (including travel and other services) and a distinguished product novelty. The digitization of retail has strained traditional sellers. The pressure also intensifies on traditional competitors to provide omnichannel solutions.
Some risk factors: (1) Costco has thrived under a variety of conditions, but as competition increases and it expands into new markets, the degree of difficulty also rises. (2) Costco handles a significant amount of customer data, and a breach could expose it to financial and reputational risk. (3) Several costs that are outside Costco’s control include wages (particularly its gaps against competitors), currency, trade policy, and the broader macroeconomic environment.